- Secondary care
- Cardiology
- Phlebology laser
- GIGAALASER
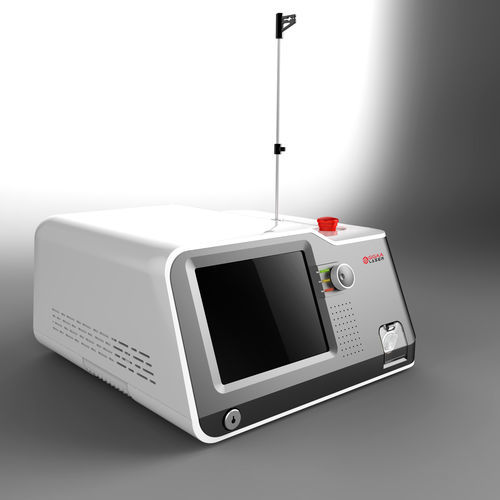
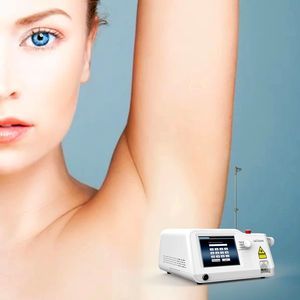
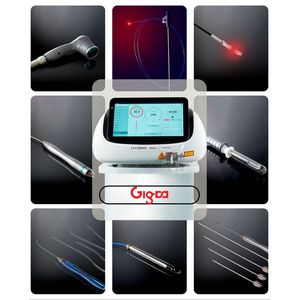
Varicose vein treatment laser phlebologyGaAsdiode

Add to favorites
Compare this product
Characteristics
- Applications
- varicose vein treatment, phlebology
- Amplifying medium
- GaAs, diode
- Ergonomics
- tabletop
- Pulse duration
- millisecond, nanosecond
- Laser class
- class 4
- Wavelength
1,940 nm
- Average power
10 W
- Weight
12 kg
(26.46 lb)
Description
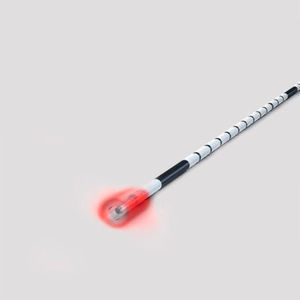
810nm, 980nm, and 1470nm are the most technologically advanced Laser diodes for EVLA in recent years. This means that there is a higher absorption of the laser energy by the interstitial water in the venous walls. It has been proven that the 1940nm laser diode has an absorption rate 40 times higher than a 1470nm laser and up to 290 times higher than the 980 nm laser.
Laser with 1940 nm wavelength provides sufficient damage to the GSV wall at a significantly lower LEED, which may have several clinical (less pain, lower incidence of paresthesia) and technical advantages (less tumescent anesthesia needed). Appropriate clinical studies will evaluate whether a 1940nm wavelength laser has significant clinical benefits to become a new standard in EVLA.
The operation is performed using a laser for EVLT, as well as a specially developed fiber instrument designed to treat a large area of the venous wall. The results of clinical studies have demonstrated the advantages of the proposed technique in comparison with phlebectomy and radiofrequency ablation, consisting of:
high efficiency of the method (complete elimination of varicose veins in 98% of patients);
excellent cosmetic result (due to a small puncture when the light guide instrument is inserted);
full outpatient treatment (operation within a maximum of 40 minutes);
absence of disability;
no painful sensations at the end of treatment.
VIDEO
Catalogs
No catalogs are available for this product.
See all of GIGAALASER‘s catalogsExhibitions
Meet this supplier at the following exhibition(s):

Related Searches
- Catheter
- Aesthetic medicine laser
- Diode laser
- Tabletop laser
- Dermatology laser
- Millisecond laser
- Urological catheter
- Class 4 laser
- Surgical laser
- Catheter guidewire
- Diagnostic catheter
- Physical therapy laser
- 5 FR catheter
- Vascular lesion treatment laser
- Dental laser
- Nanosecond laser
- Physical biostimulation laser
- Ophthalmic laser
- Lipolysis laser
- Gynecological surgery laser
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.