- Products
- Catalogs
- News & Trends
- Exhibitions
Disease risk management software Dr. Noon Fundusscreeningmedicalophthalmology

Add to favorites
Compare this product
Characteristics
- Function
- disease risk management, screening
- Applications
- medical, ophthalmology
- Area of the body
- retina
- Type
- artificial intelligence
Description
Retina-based AI solution that diagnoses retinal abnormalities
- Regulation Info
- Dr. Noon Fundus_Korea MFDS : [Product Name] DrNoon for fundus screening / [Product License No.] 제허 20-618호 / [Date of Initial Approval] 8 October 2020 / [Validity Period] 8 October 2020 – 30 November 2030 / [Issuer] The Ministry of Food and Drug Safety
- Dr. Noon Fundus_CE : EC Certificate issued under the European Medical Device Regulation (EU MDD) / [EC Certificate No.] KR21/81826550 / [First Issue Date] 11 May 2021 / [Expiry Date] 31 December 2028 / [Issuer] SGS Belgium NV
- AI-powered Solution for Diagnosing Retinal Abnormalities
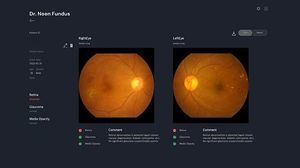
Dr. Noon Fundus is a retina-based AI diagnostic software that diagnoses retinal abnormalities. By analyzing a single retinal photograph, it automatically detects four types of retinal abnormalities: Glaucoma, Media Opacity, Age-related Macular Degeneration, Diabetic Retinopathy. Dr. Noon Fundus assists ophthalmologists, primary care physicians, and screening centers in making diagnoses related to retinal abnormalities.
- Retinal Abnormalities Detectable with Dr. Noon Fundus
- Glaucoma (Suspect): Glaucoma is a disease that damages the optic nerve in the eyes. Often known as a silent killer, if left untreated, it will lead to permanent vision loss. *Source - National Eye Institute, National Institutes of Health
- Media Opacity: A Media Opacity is a clouding of the lens in the eye that affects vision. Most Media Opacity are related to aging and are commonly found among older people. *Source - National Eye Institute, National Institutes of Health
- Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD): Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) is an age-related deterioration of the vision focal point in your eye. AMD can interfere with daily activities such as driving, reading, and writing. *Dr. Noon Fundus screens for age-related macular degeneration and the report flags it as retina normal or abnormal. *Source - National Eye Institute, National Institutes of Health
- Diabetic Retinopathy (DR): Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is a common complication of diabetes leading to severe and permanent blindness. As DR is asymptomatic in the early stages, patients may not notice any change in their vision at first. *Dr. Noon Fundus screens for Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) and the report flags it as retina normal or abnormal. *Source - National Eye Institute, National Institutes of Health
- Patient Journey
- STEP 1: Eye Scan - Take one picture of each eye to capture the retina.
- STEP 2: Image Upload - The retinal images are uploaded to the healthcare institution’s server or cloud platform.
- STEP 3: AI Analysis - Artificial intelligence automatically analyzes suspected retinal abnormalities.
- STEP 4: Result Review - Retinal abnormalities are determined through a promptly delivered report.
- Key Benefits
- High Accuracy: Based on learning from more than 100,000 retinal images verified by ophthalmology experts, we provide highly reliable diagnoses.
- Fast Test Results: The testing procedure is the same as existing retinal exams, and results are also delivered promptly.
- High Accessibility: Can be utilized in clinics, hospitals, and health screening centers, providing more patients with the opportunity to receive cardiovascular assessments.
- Our Customers
Dr. Noon Fundus is utilized by leading hospitals, clinics, and check-up centers in Korea and worldwide.
- Publications & Webinars
- Multi-categorical deep learning neural network to classify retinal images: A pilot study employing small database
- Deep Learning Is Effective for Classifying Non-referable versus Referable Eye Condition using Fundus Photographs
- Efficacy of deep learning-based artificial intelligence models in screening and referring patients with diabetic retinopathy and glaucoma
- Technical Specifications / Features
- Product Type: AI software medical device
- Function: Automatic analysis of fundus images for diagnosis of major eye diseases
- Detectable Conditions: Glaucoma (Suspect), Media Opacity, Age-related Macular Degeneration, Diabetic Retinopathy
- Regulatory Approvals: Korea MFDS, CE (EU MDD)
- First Approval: 2020 (Korea), 2021 (CE)
- Validity: Korea (2020–2030), CE (2021–2028)
- Intended Users: Ophthalmologists, primary care physicians, screening centers
- Data Source: Over 100,000 retinal images
VIDEO
Exhibitions
Meet this supplier at the following exhibition(s):

*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.