- Laboratory
- Sample management
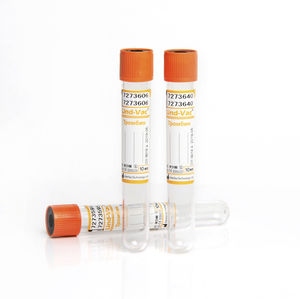
- Blood glucose analysis collection tube
- OÜ InterVacTechnology
Blood glucose analysis collection tube LIND-VAC® FE seriesround bottombloodsodium fluoride
Add to favorites
Compare this product
fo_shop_gate_exact_title
Characteristics
- Applications
- for blood glucose analysis
- Shape
- round bottom
- Sample type
- blood
- Other characteristics
- sodium fluoride, potassium oxalate, with stabilizer
- External diameter
13 mm
(0.5 in)- Height
75 mm, 100 mm
(3 in, 3.9 in)- Capacity
2 ml, 3 ml, 4 ml, 5 ml
(0.07 US fl oz, 0.1 US fl oz, 0.14 US fl oz, 0.17 US fl oz)
Description
With sodium fluoride and potassium oxalate
The tubes contain a glucose stabiliser, which allows you to block the process of glycolysis for up to 24 hours at room temperature.
Scope: research of glucose and lactate
Adding sodium fluoride and potassium oxalate to a tube helps prevent the breakdown of blood glucose (a process called glycolysis) and maintain its level in a blood sample.
Sodium fluoride and potassium oxalate act as anticoagulants, binding Ca2+ ions; in addition, sodium fluoride stabilises glucose levels.
Glucose breaks down to pyruvate and lactate with the sequential implementation of various enzymatic reactions. Sodium fluoride inhibits some enzymatic reactions, including the conversion of phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate, and prevents glycolysis.
Catalogs
No catalogs are available for this product.
See all of OÜ InterVacTechnology‘s catalogsRelated Searches
- Sample tube
- Laboratory sample tube
- Collection tube
- Cylindrical collection tube
- Blood collection tube
- Sampling kit
- Conical test tube
- Collection tube with anticoagulant
- Laboratory swab
- Sterile sample tube
- Laboratory collection tube
- Transport swab
- Graduated sample tube
- Sterile swab
- Blood test tube
- Sample storage tube
- Virus swab
- Hematological analysis collection tube
- Collection tube with clot activator
- Blood sampling kit
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.