- Products
- Catalogs
- News & Trends
- Exhibitions
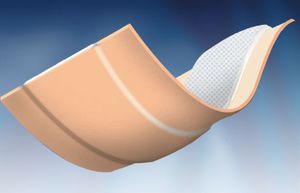
Polyester wound dressing Cure-Aid Liponon-wovennon-adherenthydrocolloid
Add to favorites
Compare this product
fo_shop_gate_exact_title
Characteristics
- Composition
- polyester
- Option
- non-woven, non-adherent, hydrocolloid
Description
They are composed of gelling non-adherent Lipo-colloid wound contact layer, comprising polyester mesh impregnated with superabsorbent powder, soft paraffin and cohesion polymers.
How does it work?
1. Paraffinic components have non polar fatty nature, so they do not adhere with the polar protenaceous exudates.
2. Hydrocolloid particles absorb exudates and turn to gel which provides optimum moist environment that enhances wound healing. Furthermore, it aids non adherence due to syn-
ergestic action between gel and paraffinic components.
3. The polyester net allows the passage of exudates to be absorbed by the absorbent layer, so excess exudates do not have time to dry at the wound bed.
Features
• Healing in moist environment:
Hydrocolloid particles gel upon absorption of wound exudates, creating moist environment in favour of wound healing.
• Painless and atraumatic removal:
Due to its fatty, yet non-greasy, nature, together with the gel formation property upon exudates contact, Lipo-colloid dressings’s removal is painless and atraumatic for the wound.
• Absorbent:
Being laminated to non-woven absorbent layer enables the dressing to manage different level of exudates.
• Instant absorption:
Exudates easily pass to absorbent layer through lipo-colloid mesh openings.
• Exudates retained even under pressure:
The pad can keep the absorbed exudates even under compression; this prevents maceration and retains a humid surface environment to facilitate wound healing.
Indications
Used as primary dressings to cover minor wounds to absorb any exudates and provide moist environment in favour of healing process.
Catalogs
No catalogs are available for this product.
See all of Pharmaplast‘s catalogsExhibitions
Meet this supplier at the following exhibition(s):

Related Searches
- Wound care
- Wound dressing
- Cotton wound dressing
- Bandage
- Elastic wound dressing
- Elastic bandage
- Sterile wound dressing
- Breathable wound dressing
- Breathable wound dressing
- Non-woven wound dressing
- Waterproof wound dressing
- Polyurethane wound dressing
- Hypoallergenic wound dressing
- Non-woven wound dressing
- Absorbant wound dressing
- Gauze bandage
- Breathable bandage
- Non-adherent wound dressing
- Antimicrobial wound dressing
- Elastic wound dressing
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.